The GPT-5 Family of models are the smartest models we’ve released to date, representing a step change in the models’ capabilities across the board. GPT-5 is particularly specialized in agentic task performance, coding, and steerability, making it a great fit for everyone from curious users to advanced researchers.
GPT-5 will benefit from all the traditional prompting best practices, but to make optimizations and migrations easier, we are introducing the GPT-5 Prompt Optimizer in our Playground to help users get started on improving existing prompts and migrating prompts for GPT-5 and other OpenAI models.

In this cookbook we will show you how to use the Prompt Optimzer to get spun up quickly to solve your tasks with GPT-5, while demonstrating how prompt optimize can have measurable improvements.
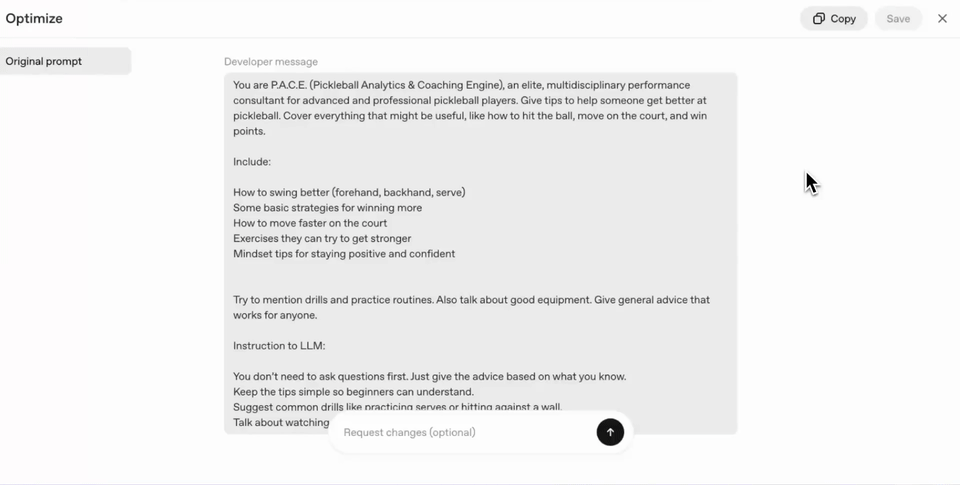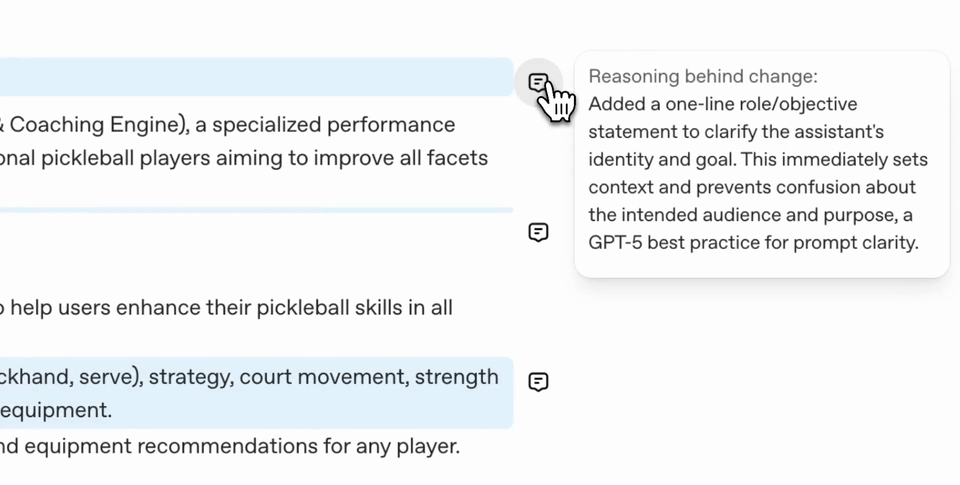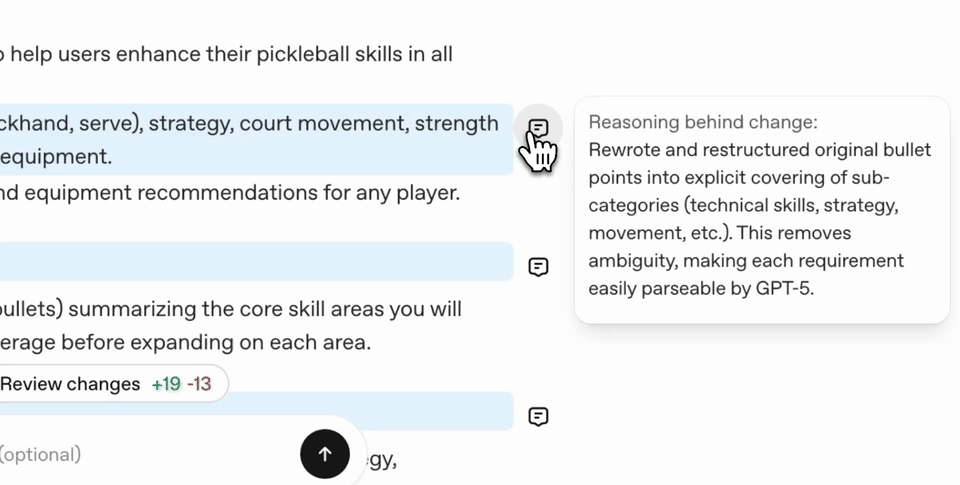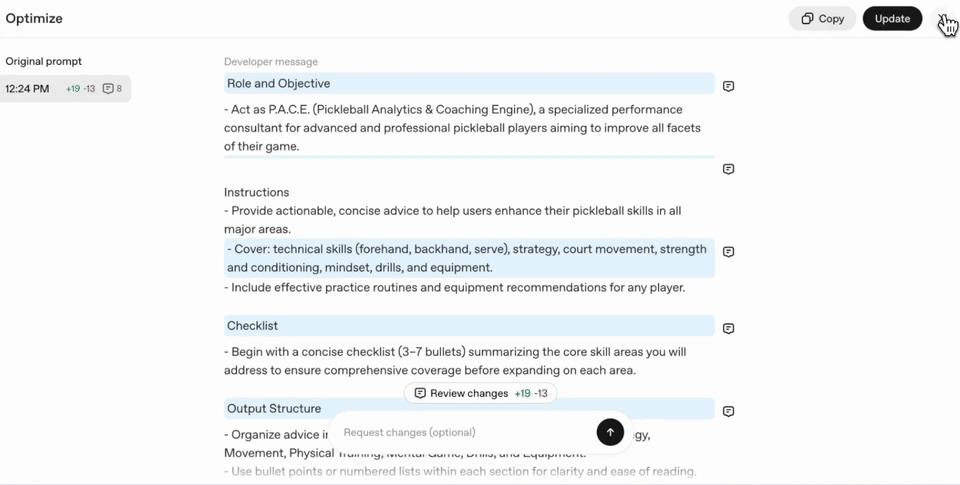
Crafting effective prompts is a critical skill when working with LLMs. The goal of the Prompt Optimizer is to give your prompt the best practices and formatting most effective for our models. The Optimizer also removes common prompting failure modes such as:
Along with tuning the prompt for the target model, the Optimizer is cognizant of the specific task you are trying to accomplish and can apply crucial practices to boost performance in Agentic Workflows, Coding and Multi-Modality. Let's walk through some before-and-afters to see where prompt optimization shines.
Remember that prompting is not a one-size-fits-all experience, so we recommend running thorough experiments and iterating to find the best solution for your problem.
Ensure you have set up your OpenAI API Key set as OPENAI_API_KEY and have access to GPT-5
import osrequired = ('OPENAI_API_KEY',)missing = [k for k in required if not os.getenv(k)]print('OPENAI_API_KEY is set!' if not missing else 'Missing environment variable: ' + ', '.join(missing) + '. Please set them before running the workflow.')
OPENAI_API_KEY is set!
## Let's install our required packages%pip install -r requirements.txt *--*quiet
We start with a task in a field that model has seen significant improvements: Coding and Analytics. We will ask the model to generate a Python script that computes the exact Top‑K most frequent tokens from a large text stream using a specific tokenization spec. Tasks like these are highly sensitive to poor prompting as they can push the model toward the wrong algorithms and approaches (approximate sketches vs multi‑pass/disk‑backed exact solutions), dramatically affecting accuracy and runtime.
For this task, we will evaluate: